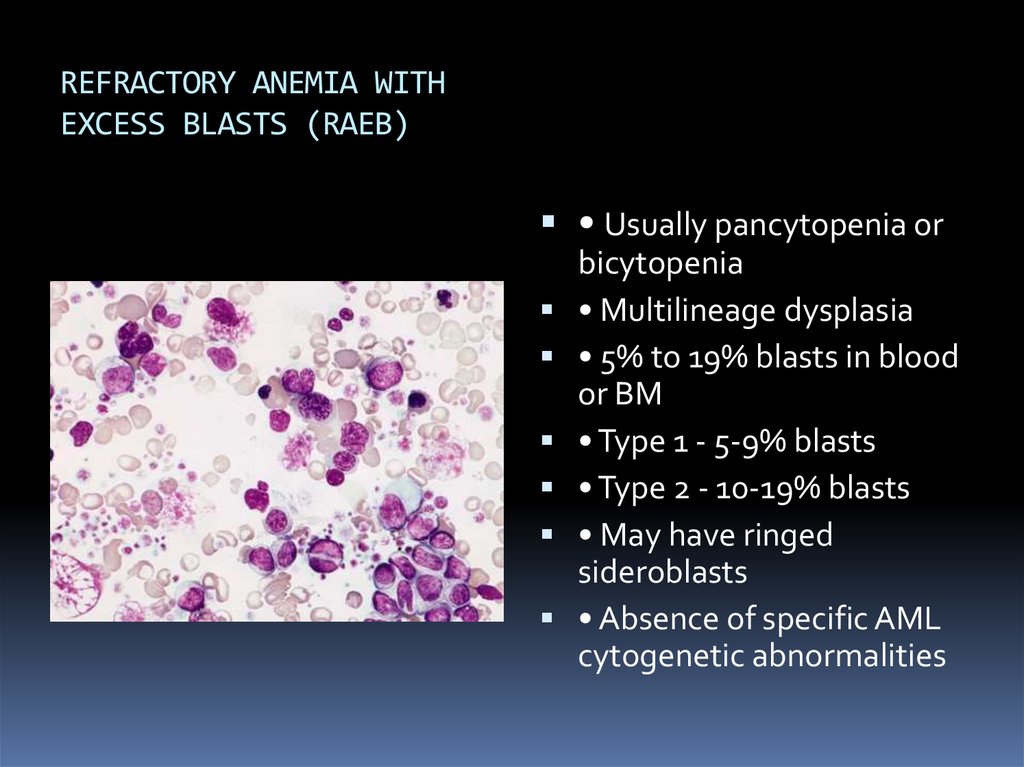
Myelodysplastic Syndrome With Excess Blasts
Myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts. Myelodysplastic syndrome MDS is a group of clonal hematopoietic disorders characterized by peripheral cytopenia and morphological abnormalities in hematopoietic cells ie myelodysplasia. Myelodysplastic Syndrome Unclassified People with this type of myelodysplastic syndrome have low levels of red blood cells white blood cells or platelets. A myelodysplastic syndrome defined by 10-19 blasts in the bone marrow or 5-19 blasts in the blood and.
23 rows Myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts is a rare type of myelodysplastic syndrome MDS. Patients with this type of MDS can often live a. There is a low survival rate of MDS and patients may only live up to a maximum of.
Find out here about the outlook and life expectancy for a person with MDS. 1 In this type of MDS the number of very early forms of blood cells blasts are increased in the bone marrow andor blood. This type of MDS is not common.
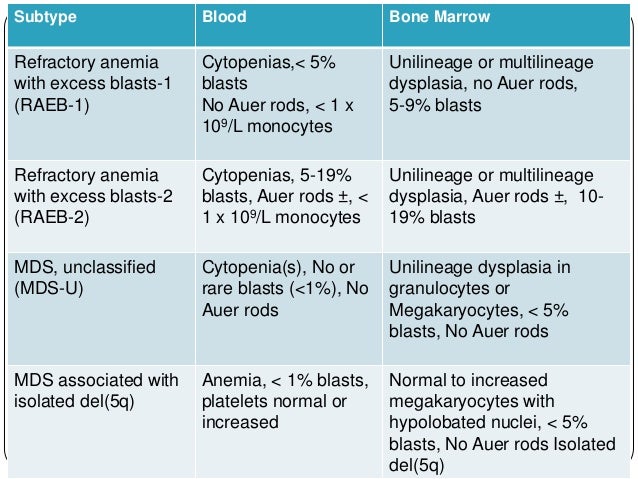
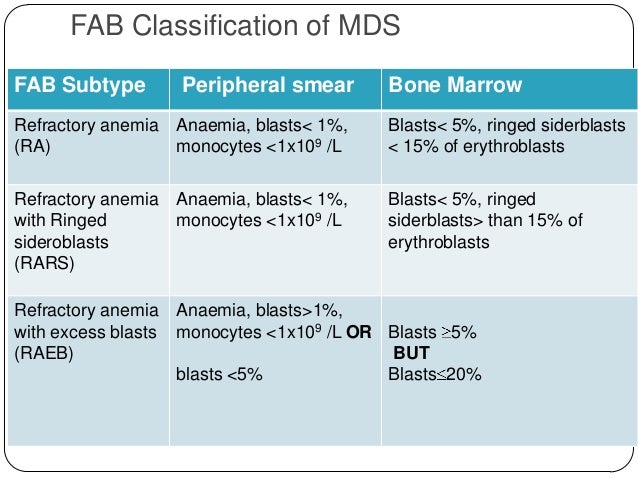
One dysplastic lineage in the bone marrow. Approximately 25 of cases progress to an acute leukemia. Refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation.
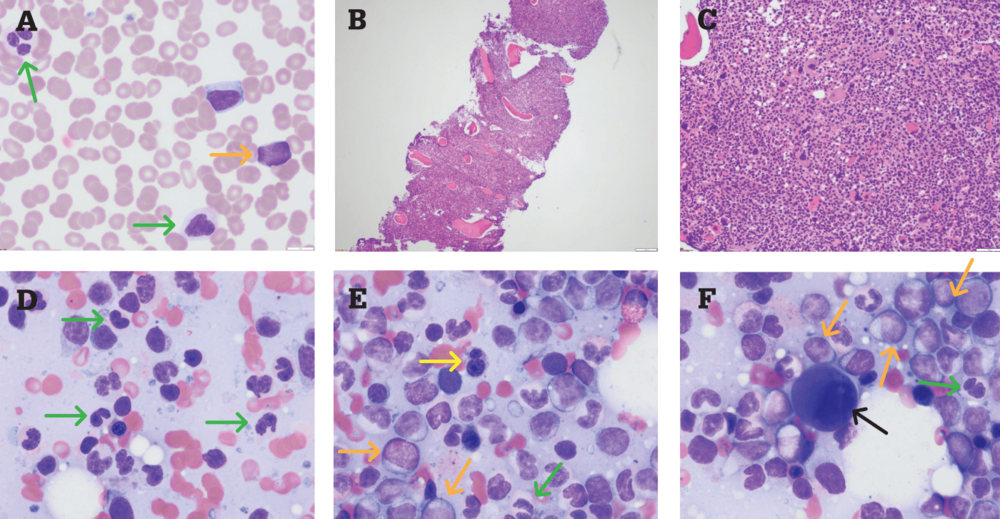
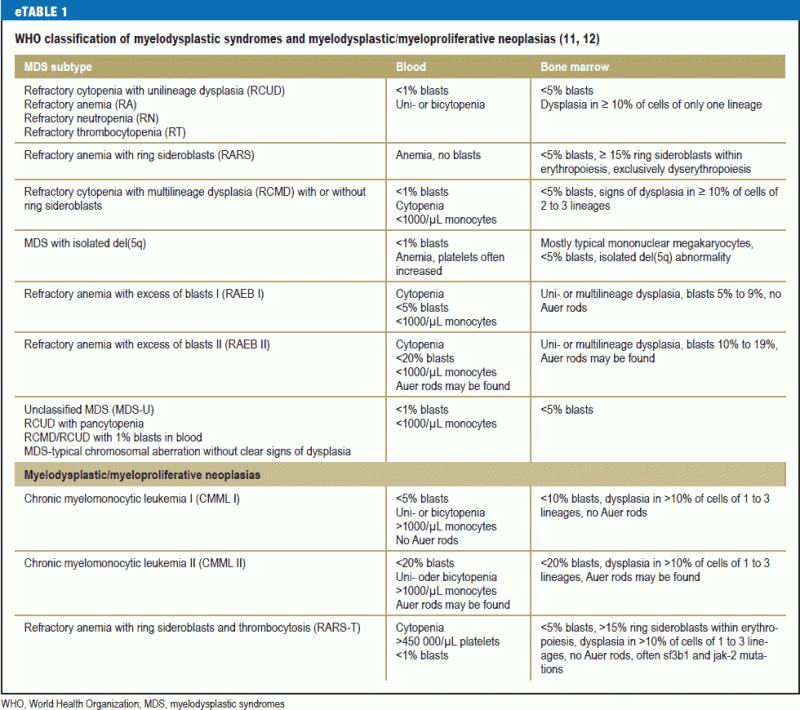
MDS with excess blasts and fibrosis MDS-EB-F is recognized as a distinct form of MDS in the newest iteration of the WHO classification 1. These abnormal blasts crowd out the healthy mature cells that your body needs. It includes two categories.
Less than 10 percent of these cells in the bone marrow look abnormal under a microscope and 5 percent of cells are blasts. Crossref Medline Google Scholar. MDS with multilineage dysplasia MDS-MLD one to.
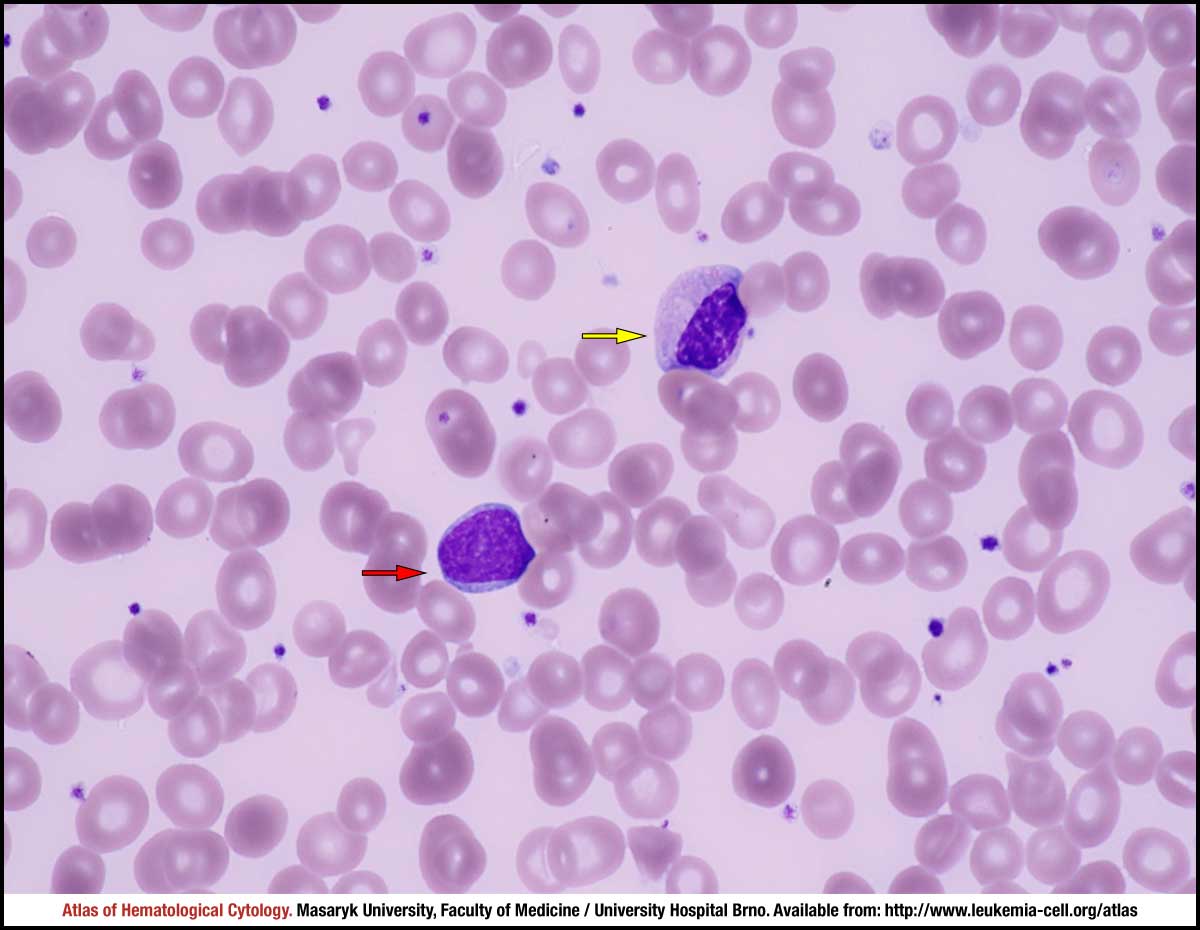
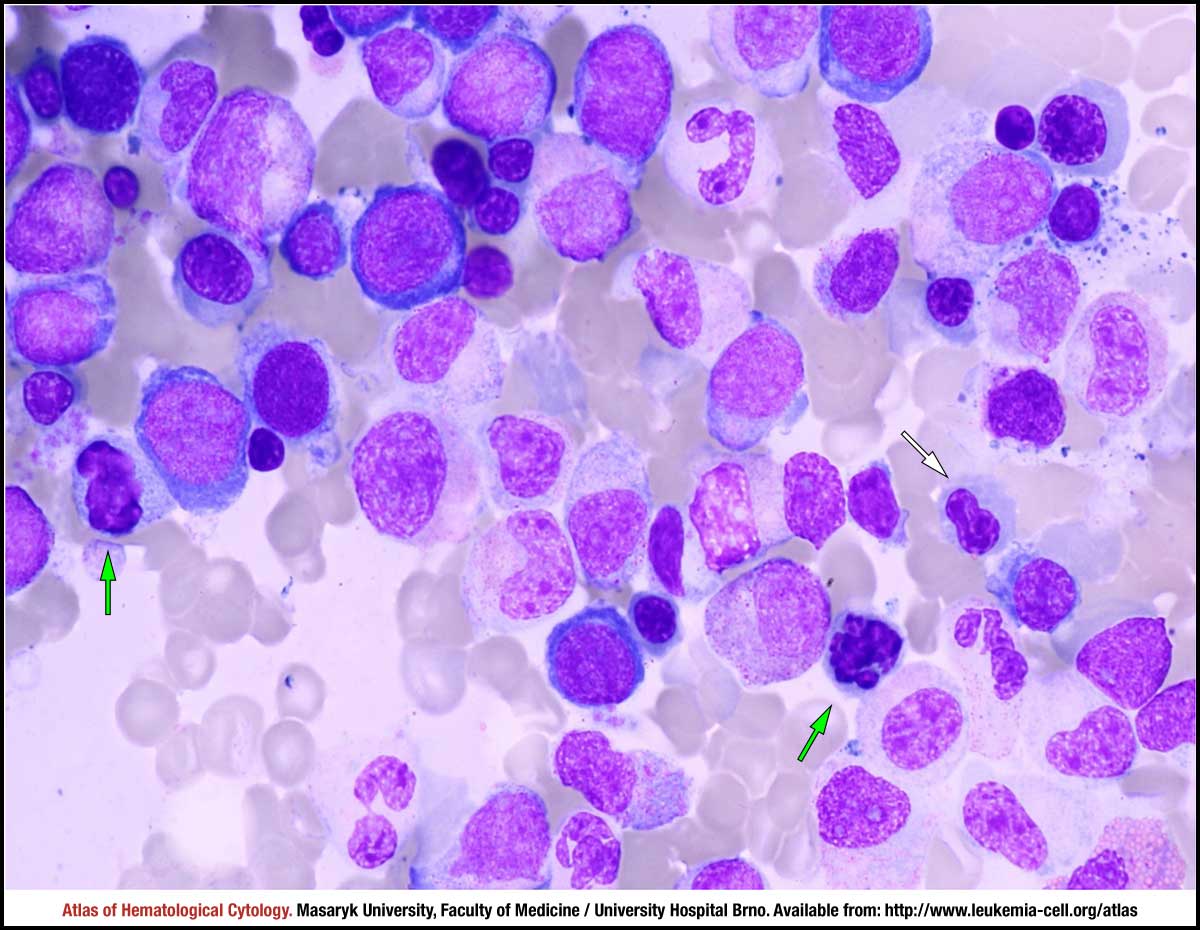
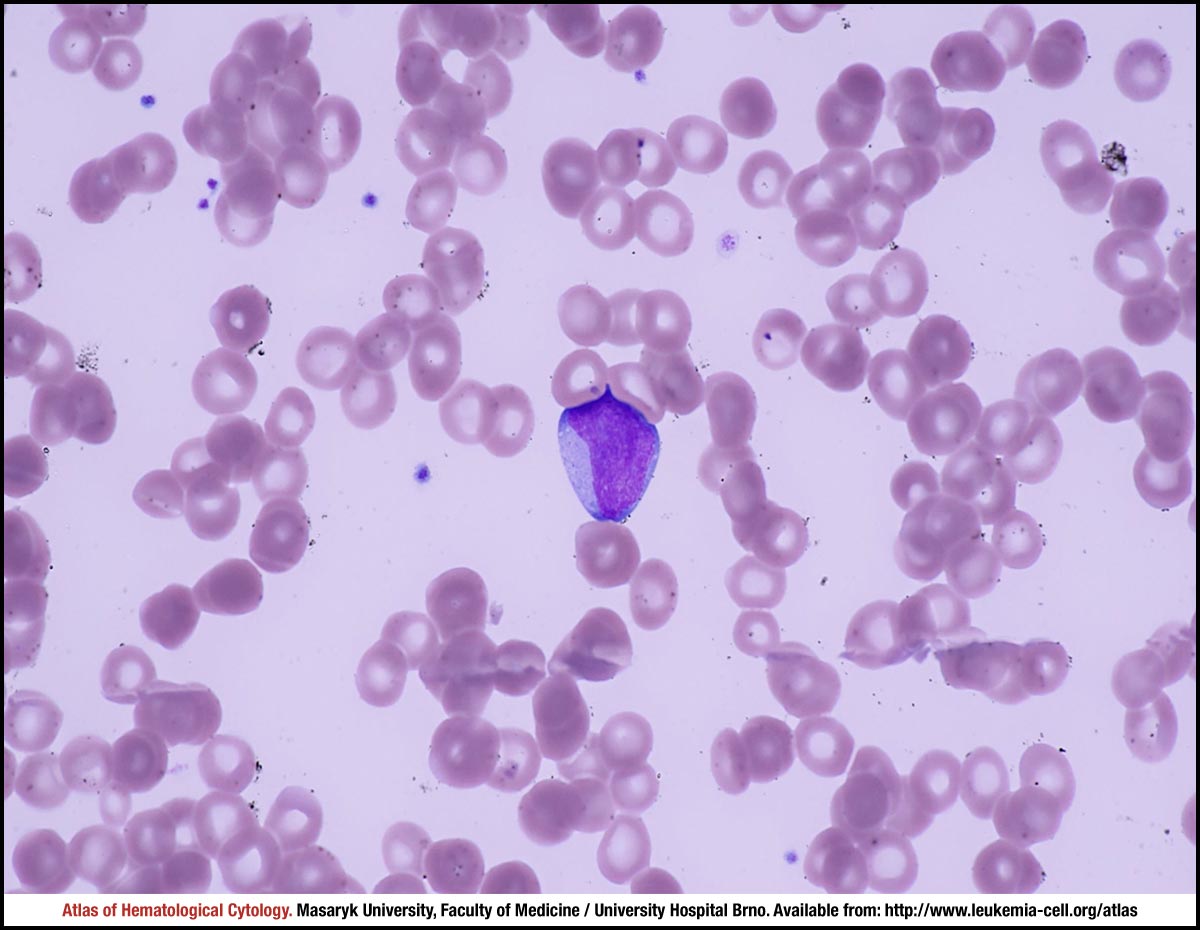
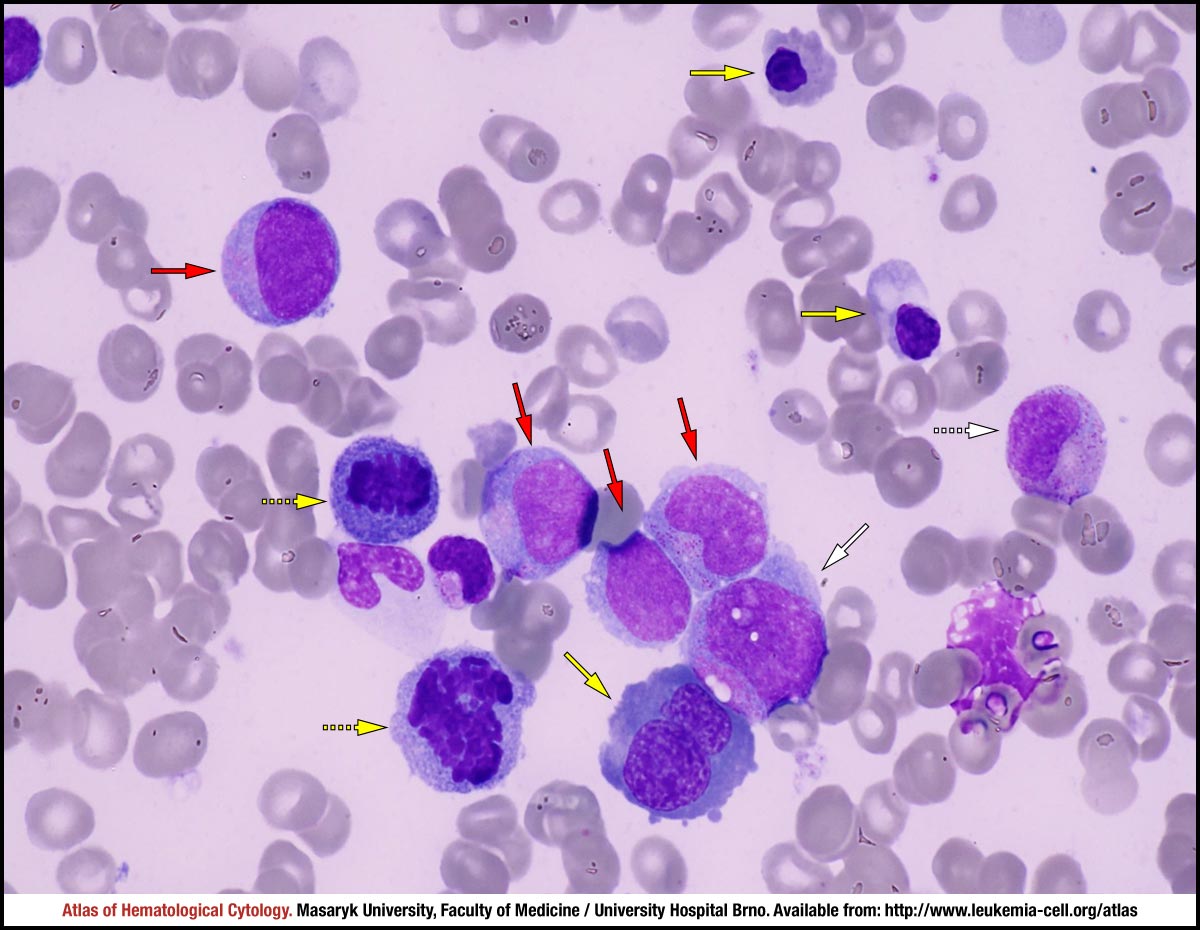
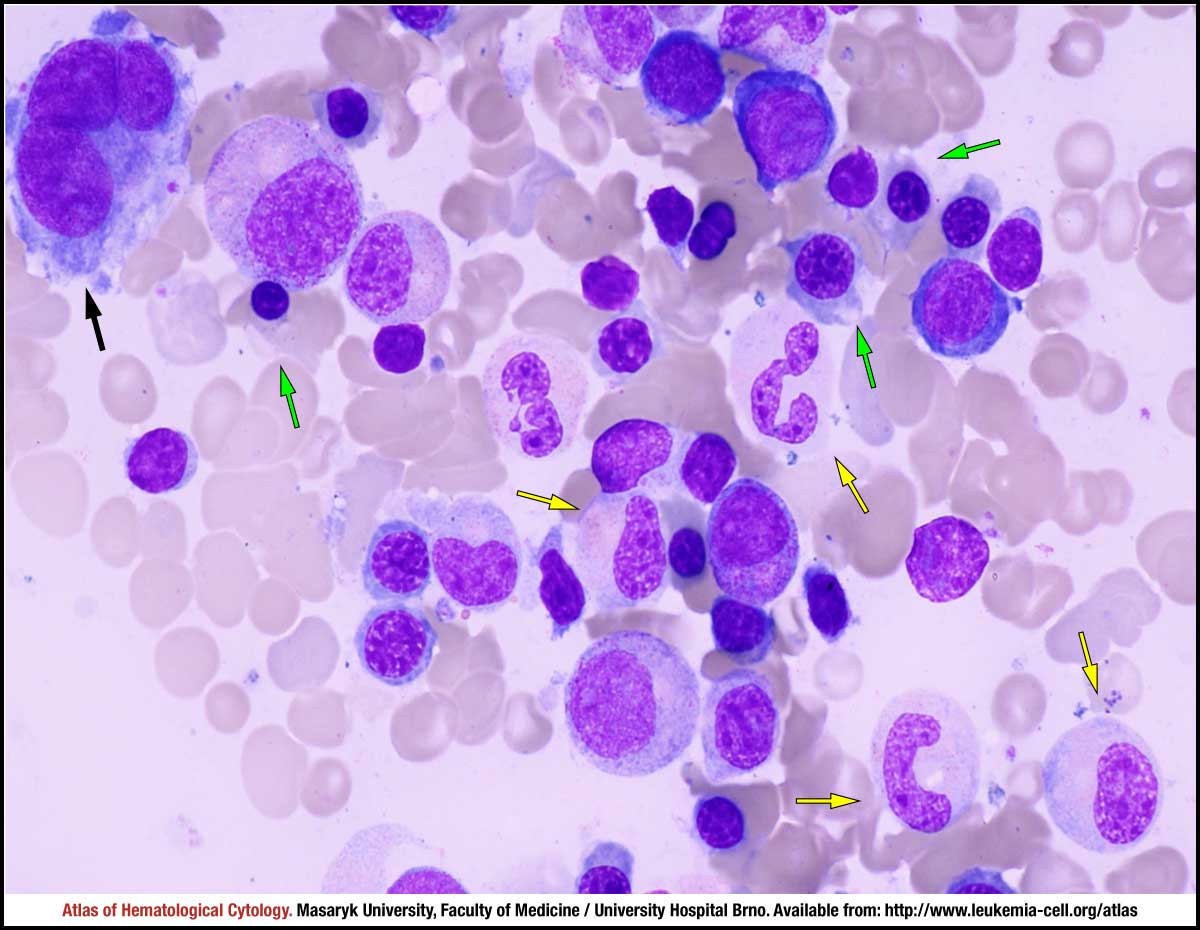
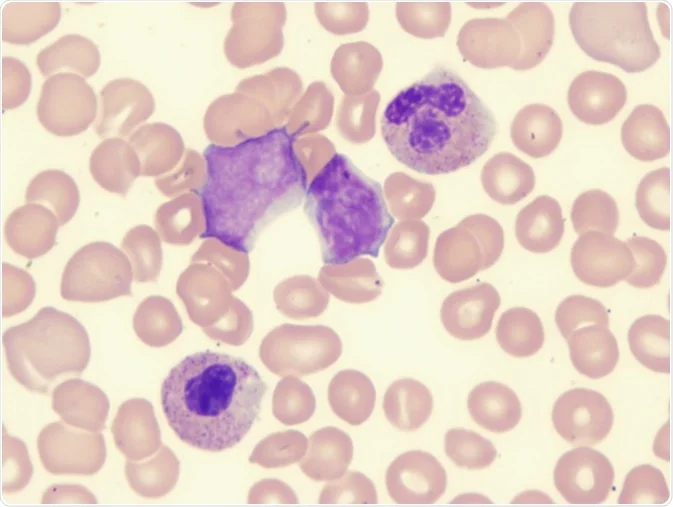
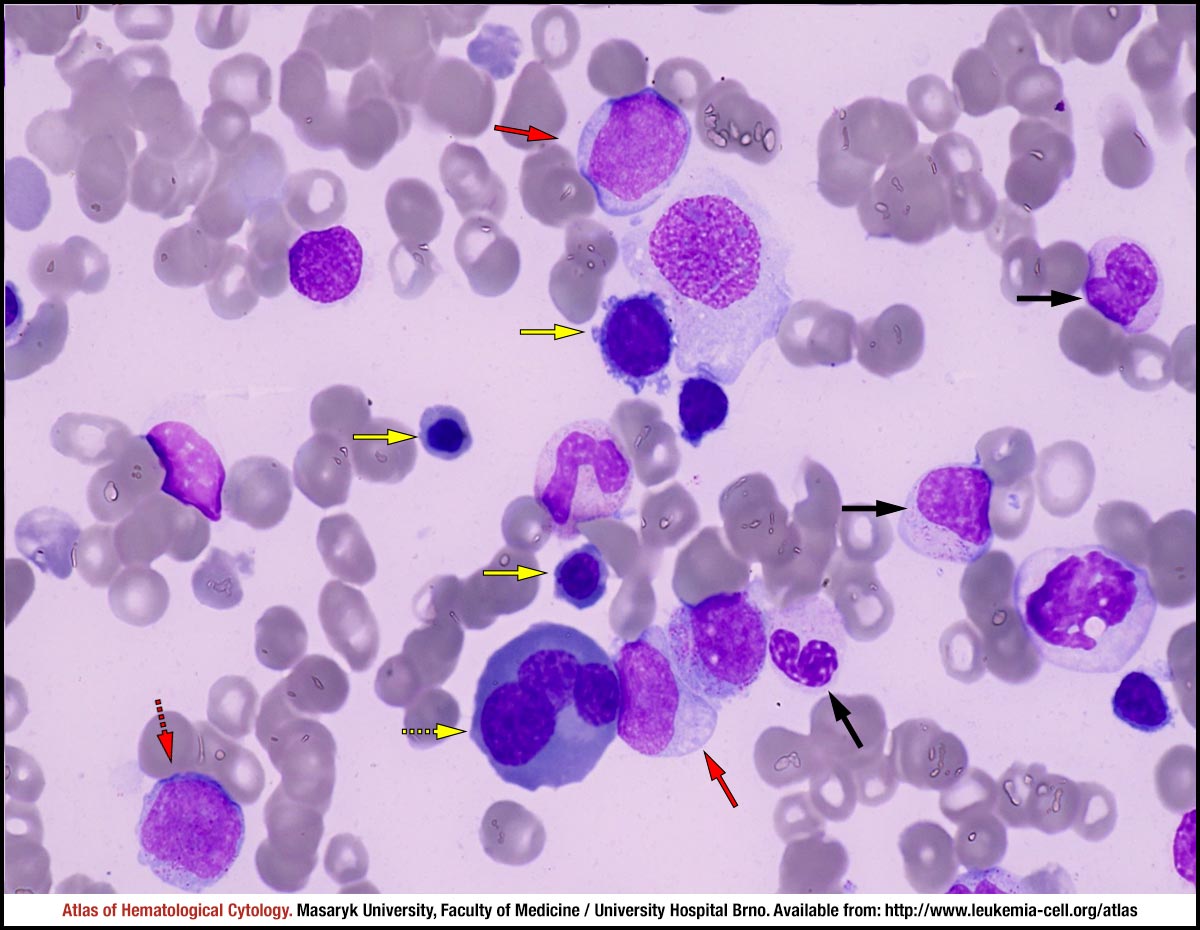
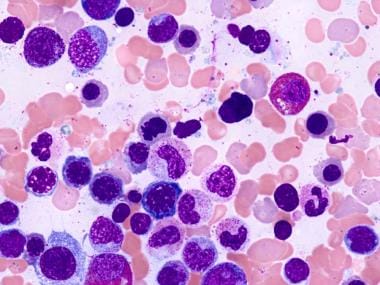
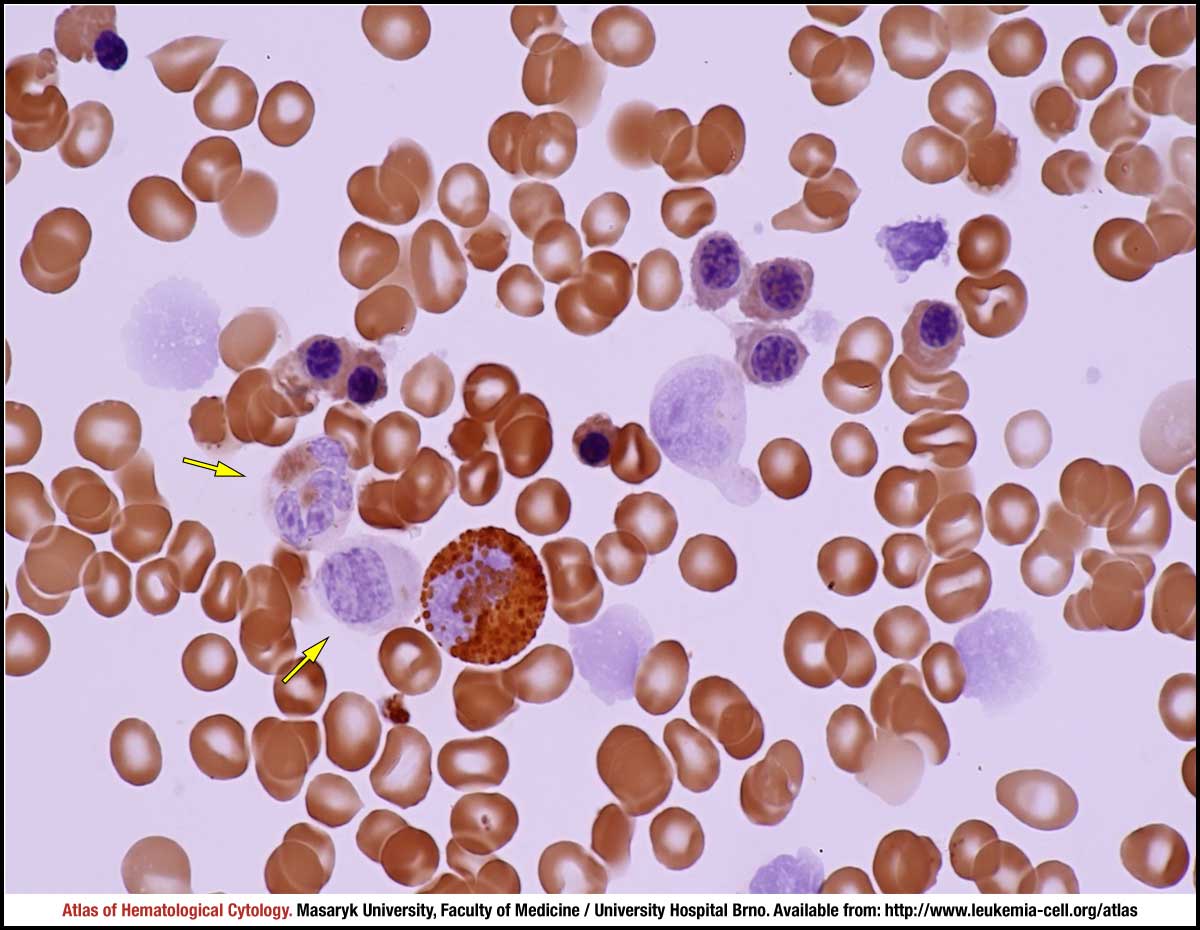
Myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts MDS-EB is a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cells HSC characterized by morphologically disordered maturation dysplasia and restricted maturation of the myeloid lineages in the bone marrow resulting in ineffective hematopoiesis cytopenias increased blasts 5-19 of blood or bone marrow nucleated cells and increased risk of progressive bone marrow failure andor developing acute myeloid. Myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts-1 Concept Id.
There is a low survival rate of MDS and patients may only live up to a maximum of.
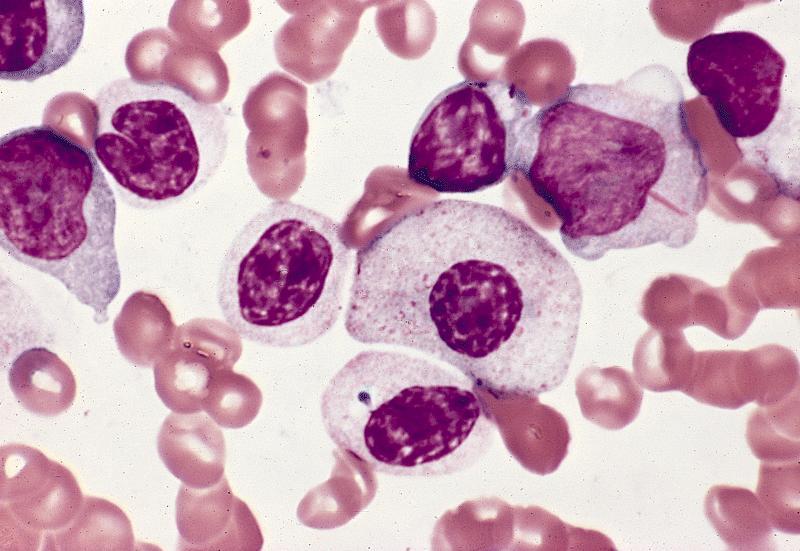
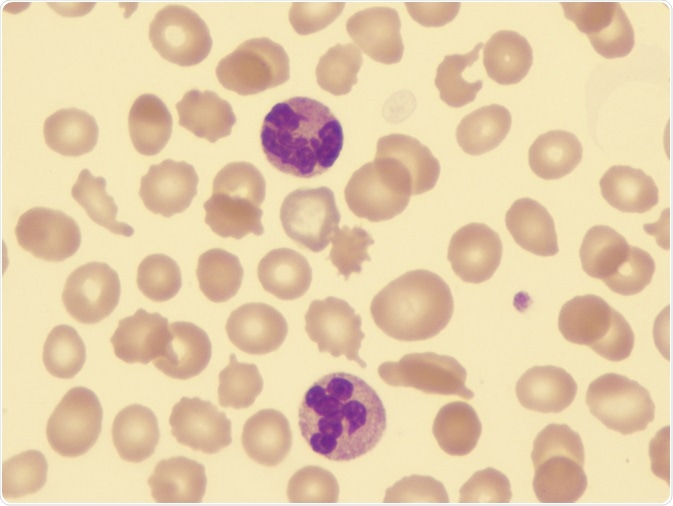
In MDS the body produces too many immature bone marrow cells also known as blasts. There is a normal number less than 5 of very early cells called blasts in the bone marrow and blasts are rare or absent in the blood. MDS with excess blasts and fibrosis MDS-EB-F is recognized as a distinct form of MDS in the newest iteration of the WHO classification 1. Approximately 33 of cases progress to acute leukemia. Comparison of myeloid blast counts and variant allele frequencies of gene mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts and secondary acute myeloid. Aging-related somatic variants acquired in the hematopoietic cells are associated with MDS pathogenesis in a. A diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts 2 MDS-EB-2 was made. These abnormal blasts crowd out the healthy mature cells that your body needs. Myelodysplastic syndrome or MDS is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow does not produce healthy cells.
Myelodysplastic Syndrome Unclassified People with this type of myelodysplastic syndrome have low levels of red blood cells white blood cells or platelets. 1 In this type of MDS the number of very early forms of blood cells blasts are increased in the bone marrow andor blood. Myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts Myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated del5q Myelodysplastic syndrome unclassifiable Refractory cytopenia of childhood Myeloid neoplasms with germline predisposition. Acute myeloid leukaemia with germline CEBPA mutation Myeloid neoplasms with germline DDX41 mutation. The early forms of cell types in the bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells or. Aging-related somatic variants acquired in the hematopoietic cells are associated with MDS pathogenesis in a. Myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts MDS-EB is a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cells HSC characterized by morphologically disordered maturation dysplasia and restricted maturation of the myeloid lineages in the bone marrow resulting in ineffective hematopoiesis cytopenias increased blasts 5-19 of blood or bone marrow nucleated cells and increased risk of progressive bone marrow failure andor developing acute myeloid.




















/myelodysplastic-syndrome-raeb-[1-bm007-1].jpeg?Width=600&Height=450&Format=4)
Post a Comment for "Myelodysplastic Syndrome With Excess Blasts"