Basal Ganglia And Parkinson's Disease
Basal ganglia and parkinson's disease. The pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease is reviewed in light of recent advances in the understanding of the functional organization of the basal ganglia BG. Basal ganglia and beyond. Current models of basal ganglia circuitry can only partially explain the cardinal symptoms in PD.
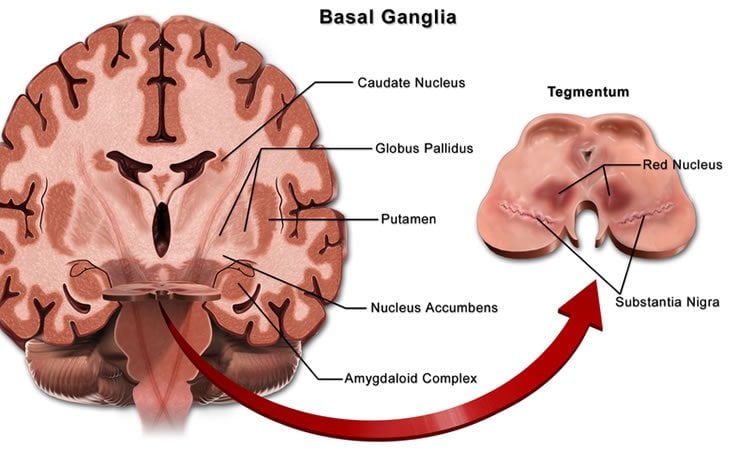
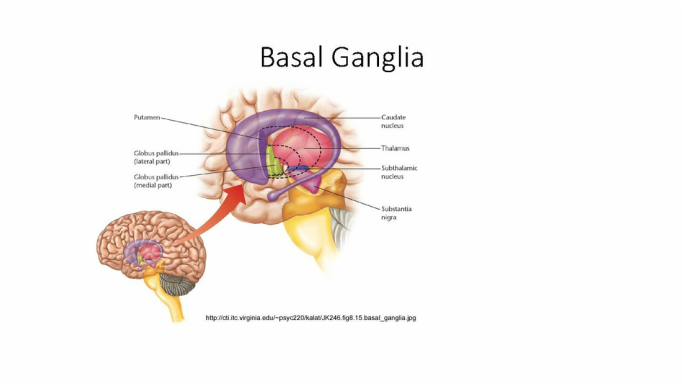
The basal ganglia circuitry processes the signals that flow from the cortex allowing the correct execution of voluntary movements. U NDERSTANDING the role and function of the basal ganglia in Parkinsons disease PD and L-dOpa- induced dyskinesia is a long-standing challenge -7. Parkinsonsdiseaseaprogressiveneurologicdisorder characterizedbytremorrigidityandslownessof movementparkinsonismwasshowninthe1960sto resultfromlossoftheneurotransmierdopamineDA withinthebasalganglia.
By A Jon Stoessl Stephane Lehericy Antonio P Strafella. The culprit of Parkinsons is the result of alpha-synuclein accumulation and aggregation within dopaminergic neurons. Current emphasis is placed on the parallel interactions between corticostriatal and corticosubthalamic afferents on the one hand and internal feedback circuits modulating BG output.
Parkinsons disease is characterized by a loss of dopaminergic innervation in the basal ganglia leading to complex motor and non-motor symptoms. The neuronal circuitry to which the basal ganglia belong. Clinical symptom alleviation through dopaminergic medication and deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus likely depends on a complex interplay between converging basal ganglia pathways.
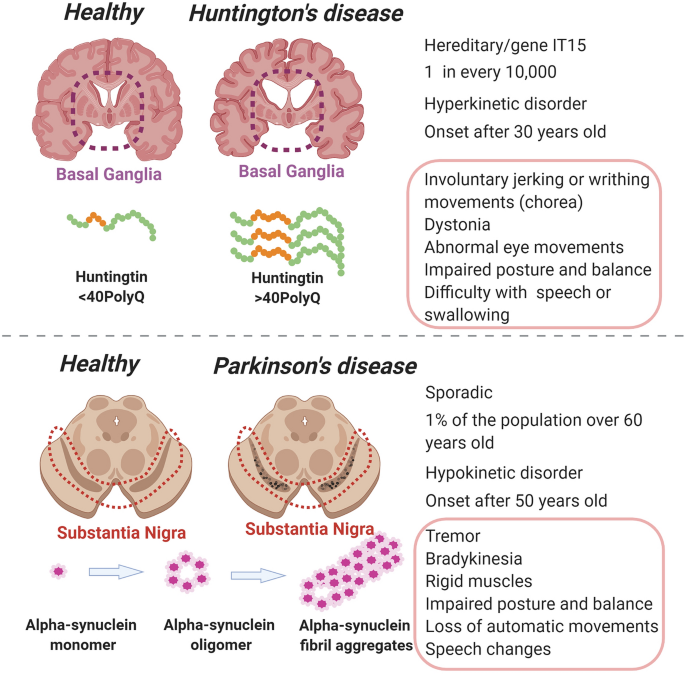
Basal ganglia and beyond. These ag gregates are named Lewy bodies Diagram below shows a neuronal cell on the left and red-deposits simulate the accumulation of Lewy Bodies on the. Strategic Programs for Innovative Research Field 1Supercomputational Life Science httpwwwsclsrikenjpenIf you wish to ask about this material please.
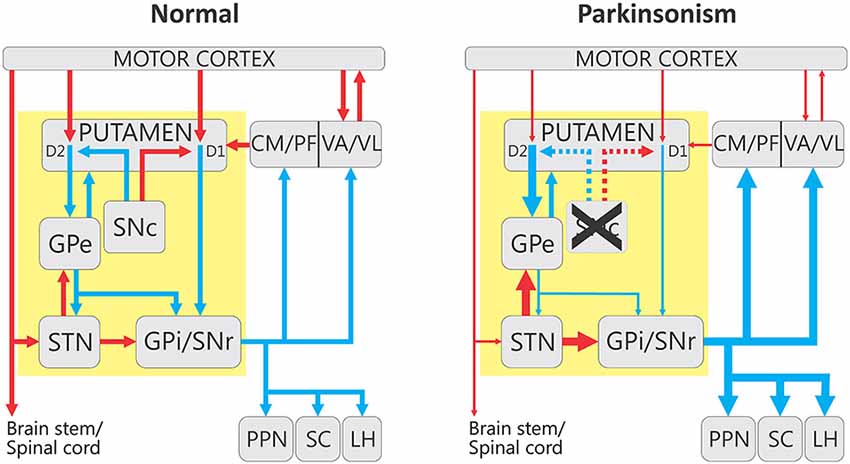
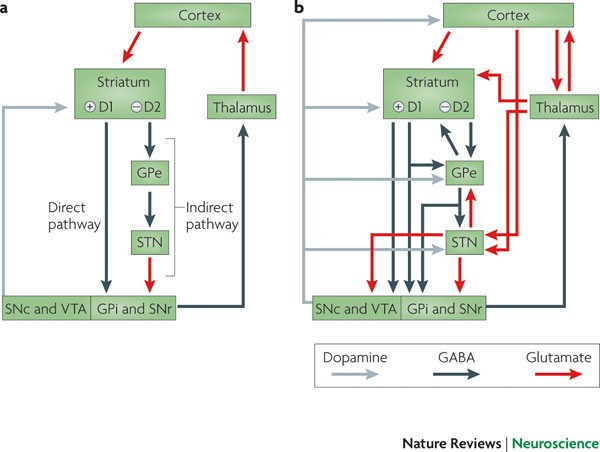
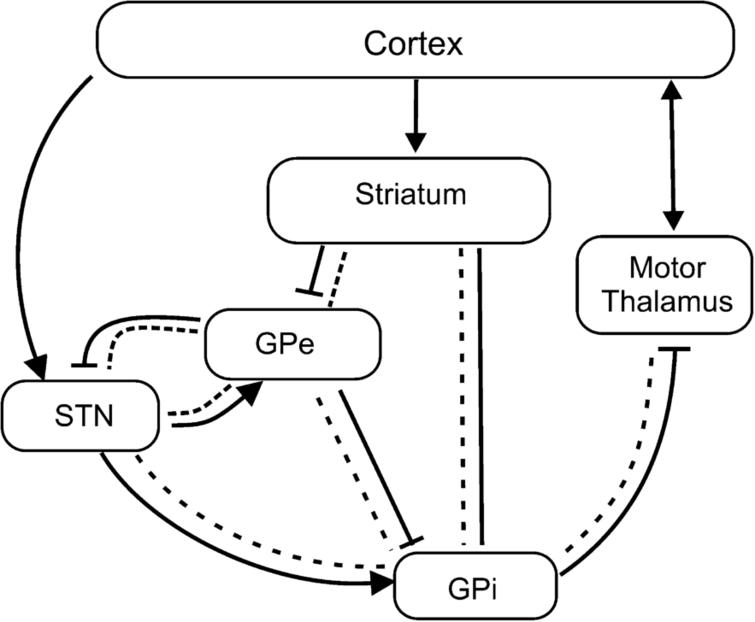
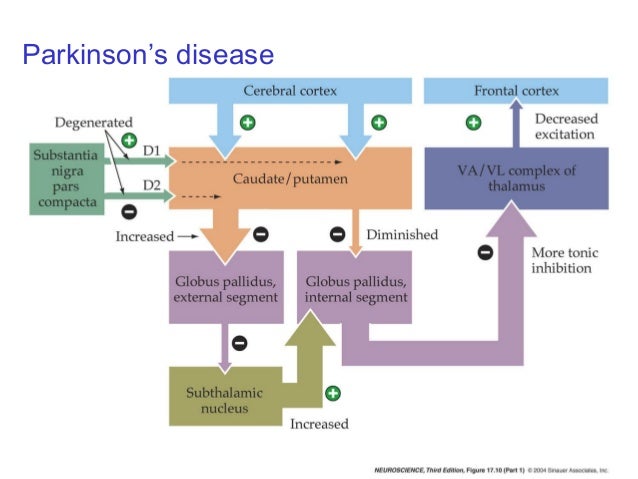
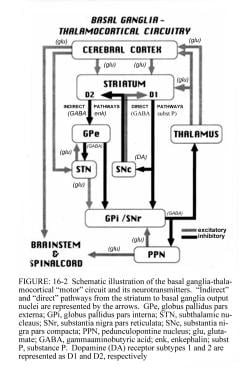
Both the direct and indirect pathways finish in the thalamus but their effects on the thalamus are very different. Here we review these recent advances with an emphasis on novel discoveries from studies of learning in patients with Parkinsons disease. The interplay between motor and cognitive aspects in Parkinsons disease rehabilitation Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
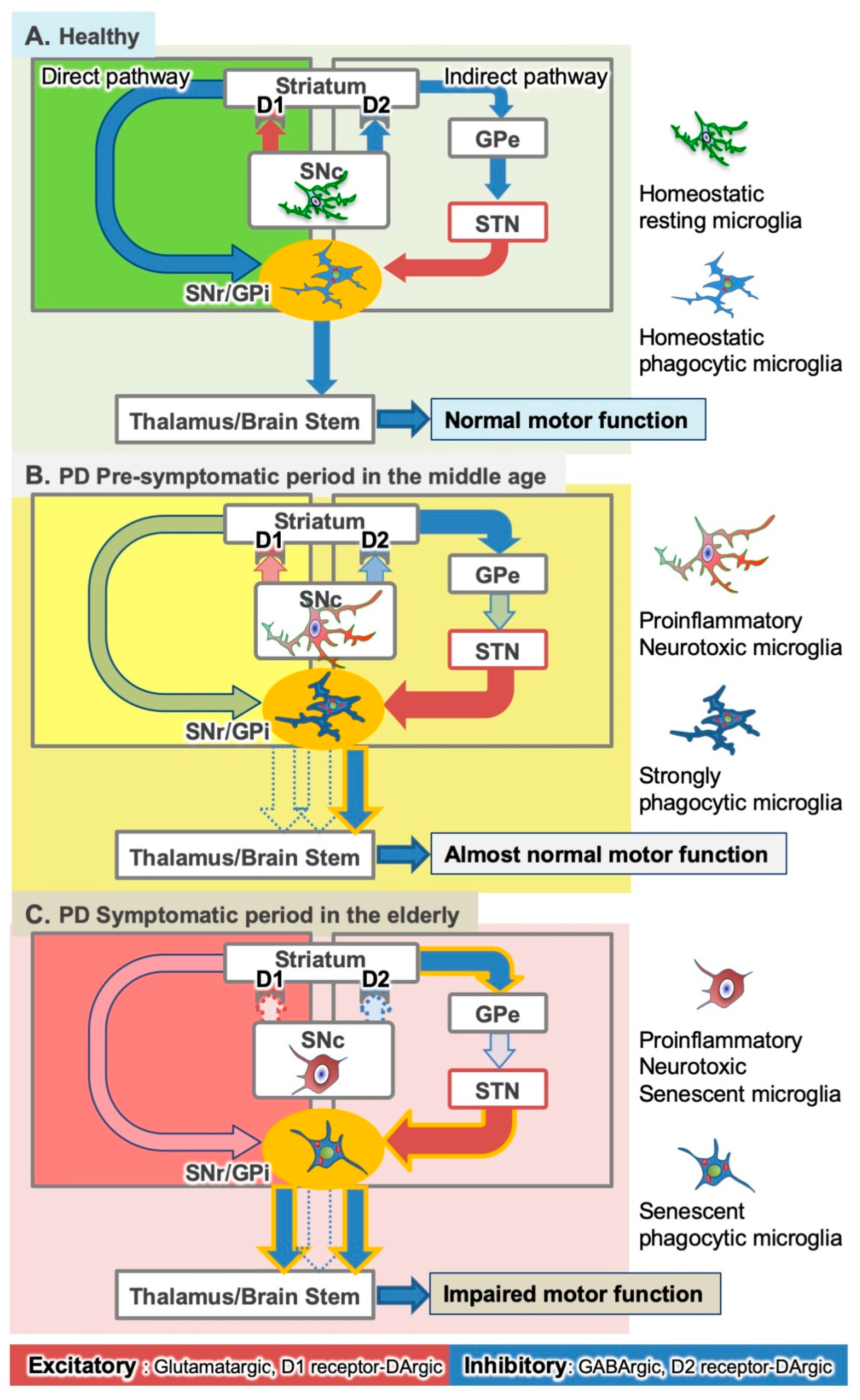
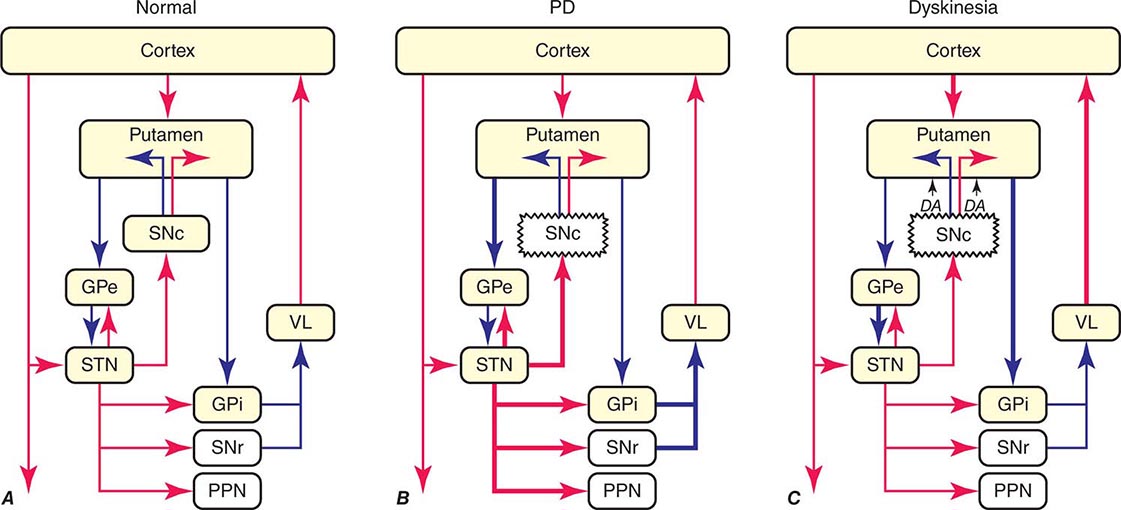
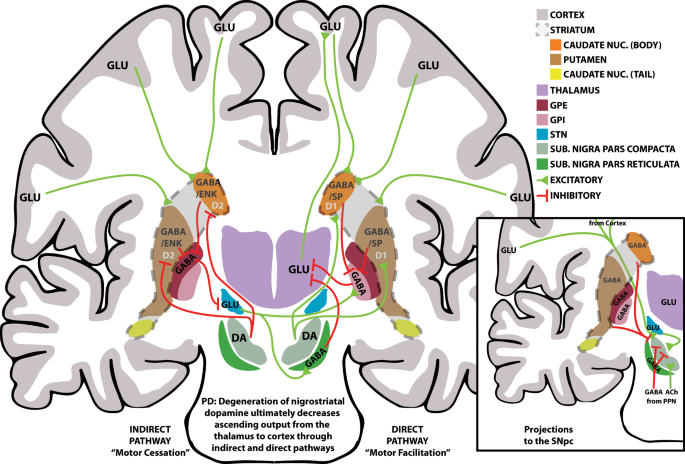
In the late 1980s a model was proposed to explain how the basal ganglia are organized and how dopamine deficiency leads to. In Parkinsons disease the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta triggers a cascade of functional changes.
The basal ganglia circuitry processes the signals that flow from the cortex allowing the correct execution of voluntary movements.
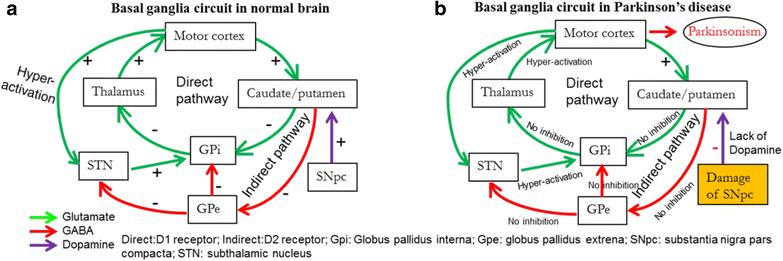
Imaging insights into basal ganglia function Parkinsons disease and dystonia. The pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease is reviewed in light of recent advances in the understanding of the functional organization of the basal ganglia BG. Basal ganglia and beyond. Excitatory signals green and inhibitory signals red in the basal ganglia in both a normal brain and one with Parkinsons disease. Parkinsonsdiseaseaprogressiveneurologicdisorder characterizedbytremorrigidityandslownessof movementparkinsonismwasshowninthe1960sto resultfromlossoftheneurotransmierdopamineDA withinthebasalganglia. These conditions include head trauma brain tumors infections in the brain and stroke. This loss of dopamine in the basal ganglia results in the motor dysfunction that characterizes Parkinsons. In Parkinsons disease the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta triggers a cascade of functional changes. Both the direct and indirect pathways finish in the thalamus but their effects on the thalamus are very different.
Functional changes of the basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinsons disease. By A Jon Stoessl Stephane Lehericy Antonio P Strafella. Functional changes of the basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinsons disease. The basal ganglia circuitry processes the signals that flow from the cortex allowing the correct execution of voluntary movements. Functional changes in basal ganglia circuitry are responsible for the major clinical features of Parkinsons disease PD. Basal ganglia and beyond. These conditions include head trauma brain tumors infections in the brain and stroke.































:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13859/Connections_of_basal_ganglia_-_hyperdirect_pathway.png)


Post a Comment for "Basal Ganglia And Parkinson's Disease"